Understanding the Mpox Emergency: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
The sudden rise in cases of Mpox, a disease formerly known as monkeypox, has drawn global attention, prompting health authorities to declare it a public health emergency. This blog provides a comprehensive guide on Mpox, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Whether you're looking to protect yourself, your family, or your community, understanding Mpox is crucial in staying safe.
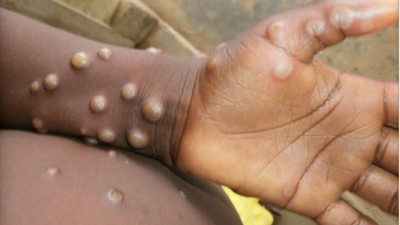
What is Mpox?
Mpox is a viral zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. It belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox, known as the Orthopoxvirus genus. While Mpox is less severe than smallpox, it can still lead to serious health complications, particularly in vulnerable populations.
The virus was first discovered in 1958 when two outbreaks occurred in colonies of monkeys kept for research, hence the name "monkeypox." The first human case was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Since then, Mpox has primarily been reported in central and western African countries, but recent outbreaks have shown that the virus can spread globally.
Causes of Mpox
Mpox is caused by the Mpox virus, which is transmitted to humans through close contact with an infected animal or human. The primary sources of infection include:
- Animal-to-Human Transmission: This occurs through direct contact with blood, bodily fluids, or cutaneous or mucosal lesions of infected animals. Wild animals, such as rodents and primates, are common carriers of the virus.
- Human-to-Human Transmission: The virus can spread from person to person through respiratory droplets, direct contact with skin lesions, or contact with contaminated materials such as bedding or clothing.
- Contaminated Objects: The virus can survive on surfaces and objects, leading to indirect transmission if a person touches a contaminated item and then touches their face or an open wound.
Symptoms of Mpox
Mpox symptoms typically appear 7 to 14 days after exposure to the virus but can range from 5 to 21 days. The disease progresses through two stages: the prodromal stage and the rash stage.
- Prodromal Stage: This early stage is characterized by flu-like symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Back pain
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes (a key feature distinguishing Mpox from other similar diseases like smallpox)
- Rash Stage: The most distinctive symptom of Mpox is a rash that usually begins on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body, including the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash progresses through several stages:
- Macules: Flat, discolored spots on the skin
- Papules: Raised bumps
- Vesicles: Fluid-filled blisters
- Pustules: Pus-filled lesions
- Scabs: The lesions eventually crust over and fall off
The entire cycle, from the onset of symptoms to the scabbing of lesions, typically lasts 2 to 4 weeks. Most people recover fully, but severe cases can occur, especially in children, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Diagnosis of Mpox
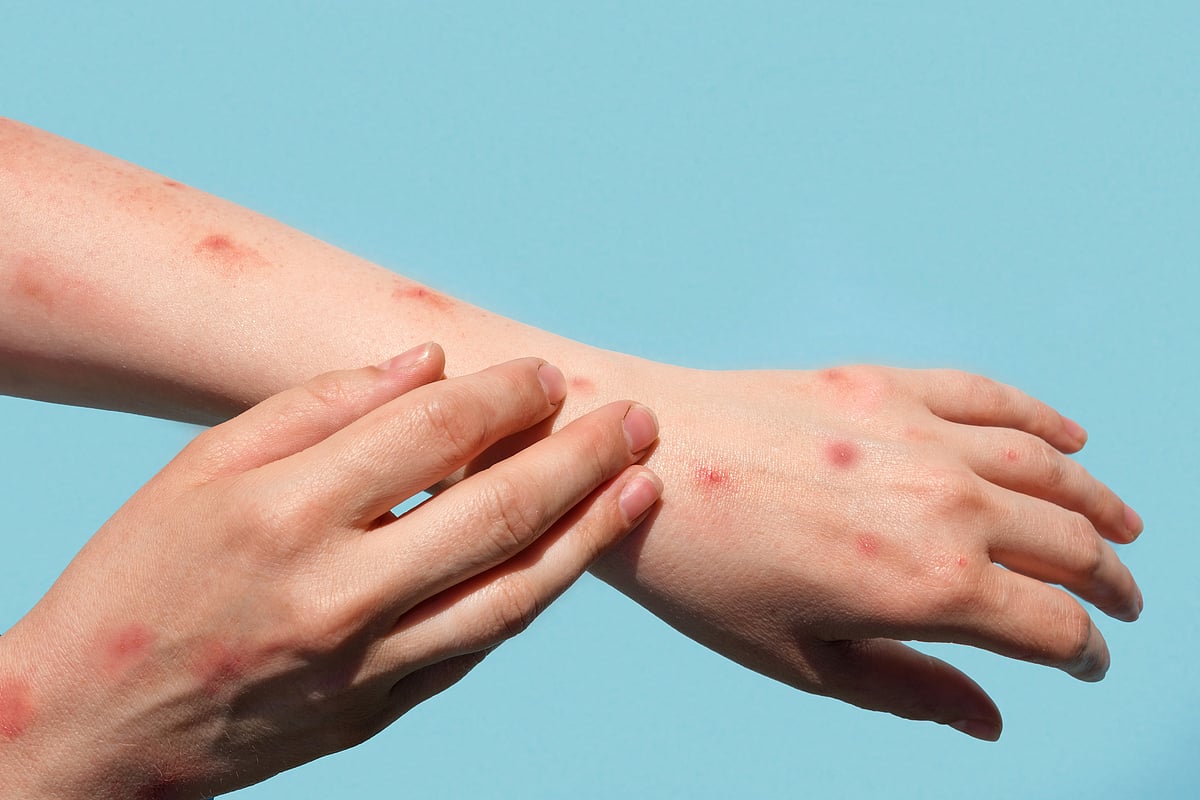
Diagnosing Mpox involves a combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers will look for the characteristic rash and inquire about potential exposure to the virus. To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are conducted on samples taken from skin lesions, blood, or respiratory secretions.
Treatment of Mpox
There is no specific antiviral treatment for Mpox, but supportive care can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment typically focuses on:
- Pain Relief: Medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce fever.
- Hydration: Ensuring the patient stays well-hydrated is crucial, especially if they have a fever or are experiencing vomiting or diarrhea.
- Skin Care: Keeping the skin clean and dry, using soothing ointments, and avoiding scratching can help prevent secondary infections.
In severe cases, antiviral medications like Tecovirimat (ST-246), originally developed for smallpox, may be used under compassionate use protocols. Vaccinia immune globulin (VIG) can also be considered for people with severe immunodeficiency or those exposed to the virus who are at high risk of severe disease.
Prevention of Mpox
Preventing Mpox involves a combination of strategies, including vaccination, public health measures, and personal protective behaviors.
- Vaccination: The smallpox vaccine has been shown to be effective in preventing Mpox, particularly in high-risk populations. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccination for people who have been exposed to the virus or are at high risk, such as healthcare workers and laboratory personnel.
- Avoiding Contact with Infected Animals: Reducing contact with animals that may carry the virus, particularly in endemic regions, is essential. This includes avoiding handling sick or dead animals and refraining from consuming bushmeat.
- Practicing Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer can reduce the risk of infection. Avoid touching your face, especially the eyes, nose, and mouth, after contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Safe Handling of Contaminated Materials: If caring for someone with Mpox, it’s important to handle contaminated clothing, bedding, and other materials with care. Wear gloves and wash your hands thoroughly after handling these items.
- Isolation of Infected Individuals: Infected individuals should be isolated from others to prevent the spread of the virus. Healthcare workers should use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when treating patients.
- Awareness and Education: Public health campaigns aimed at educating communities about Mpox and its transmission can play a critical role in prevention. Knowledge of the disease helps people take the necessary precautions to protect themselves and others.
Mpox in the Global Context
The recent Mpox outbreaks have highlighted the potential for the virus to spread beyond its traditional geographic boundaries. Factors such as increased travel, urbanization, and changes in human-animal interactions contribute to the spread of zoonotic diseases like Mpox.
Public Health Response to the Mpox Emergency
In response to the Mpox emergency, global health organizations have taken several steps to contain the spread of the virus and protect public health. These measures include:
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Enhanced surveillance systems have been established to detect and report new cases promptly. This allows for quick response and containment efforts.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Targeted vaccination campaigns are being conducted in affected areas, focusing on high-risk populations.
- Public Health Guidelines: WHO and other health authorities have issued guidelines on infection control, treatment, and prevention to healthcare providers and the public.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research aims to better understand the virus, develop effective treatments, and improve diagnostic tools.
- International Collaboration: Countries are working together to share information, resources, and expertise to combat the Mpox emergency. This collaborative approach is essential in controlling the spread of the virus and preventing future outbreaks.
The Future of Mpox: What Lies Ahead?
As the world continues to grapple with the Mpox emergency, it’s clear that ongoing vigilance and preparedness are crucial. While the current outbreak has raised awareness of the disease, it also underscores the need for sustained efforts in public health, research, and global cooperation.
In the coming years, we can expect to see continued advancements in the development of vaccines and treatments for Mpox, as well as improved strategies for surveillance and containment. Public health education will remain a key component in preventing future outbreaks, ensuring that individuals and communities are equipped with the knowledge and tools to protect themselves.
Conclusion
Mpox is a serious viral disease that has recently emerged as a global public health concern. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies is essential for protecting yourself and others from this potentially dangerous virus. By staying informed and taking appropriate precautions, we can work together to control the spread of Mpox and safeguard public health.

 Cricket Score Counter
Cricket Score Counter Heads or Tails
Heads or Tails
You have not logged in, please Login to comment.